Industry
This section covers mitigation options for industry. There are many opportunities to reduce fossil fuel use in this sector:
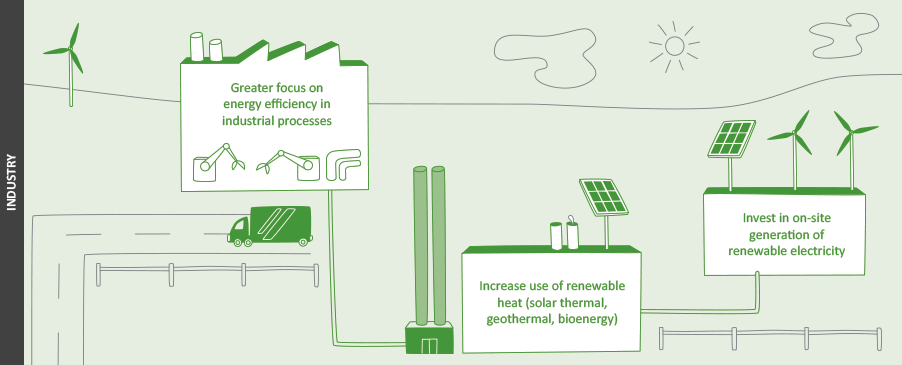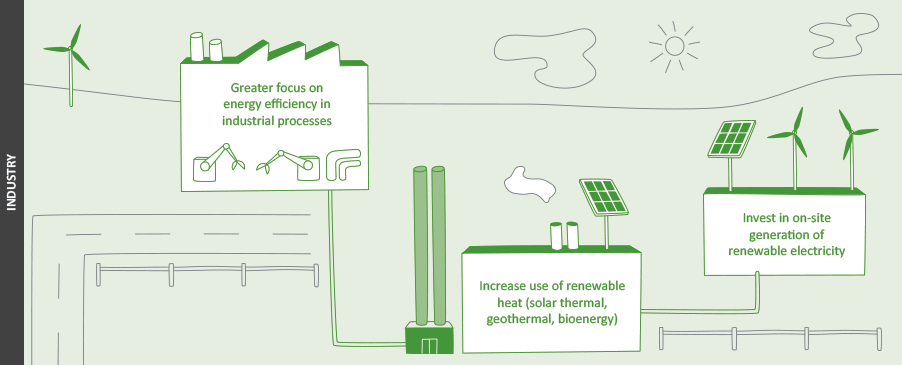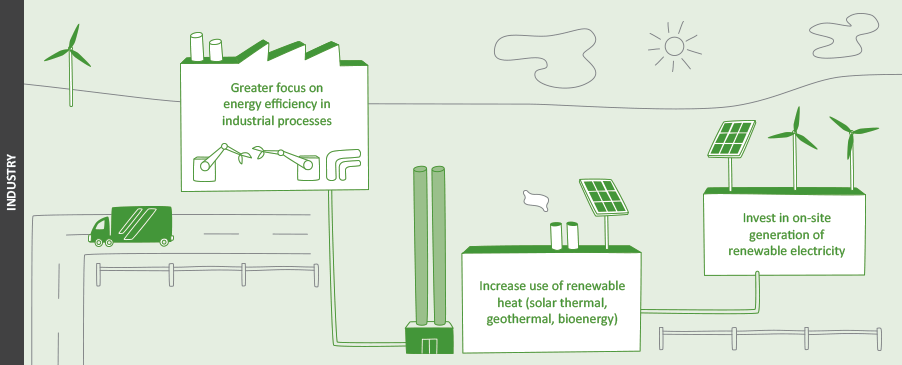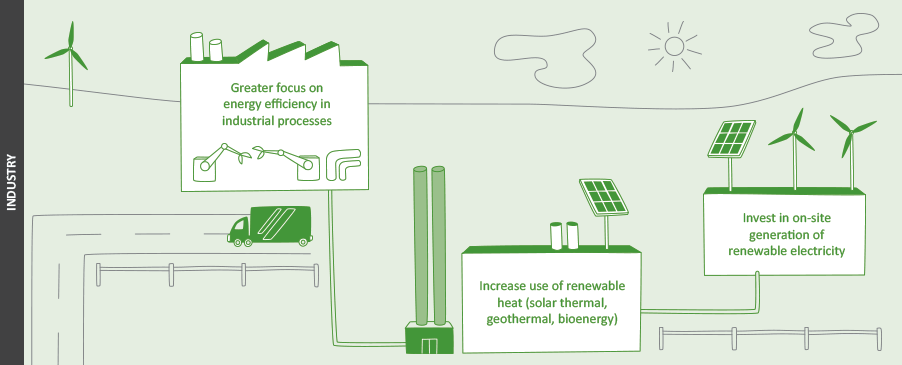
- The present dependence on burning coal and natural gas for process heat can be displaced by bioenergy, geothermal, solar thermal and electro-thermal technologies.
- Energy efficiency initiatives can reduce GHG emissions significantly but may need further incentivising to meet the short investment time frame of businesses.
- Carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) could be an option in the long term and, if coupled with bioenergy (BECCS), would give negative GHG emissions.
In pictures
Key findings
- The industrial sector directly produces 6.3% of our gross emissions (5 Mt CO2eq), mainly from cement and steel manufacture and HFCs from solvents and refrigerants.
- A similar amount of indirect emissions comes from the electricity consumed by industry plus fossil fuel combustion to raise process heat (with around 45% of that coming from coal).
- There are few technology barriers to the use of renewable heat energy in most instances and high potential to displace fossil fuels. For locations where biomass or geothermal resources are limited or costly, it may currently be uneconomic or there may be concerns over security of supply. Investment decisions require an evaluation of the long-term availability of the fuel required for the heat plant installed, even where biomass process residues and wastes are produced on-site.
- Industries which have large single point sources of emissions have the opportunity to consider carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) measures in the future if and when they become cost effective under a high carbon price. Potentially on-site bio-energy generation liked with carbon dioxide capture and storage (BECCS) could physically remove CO2 from the atmosphere.
Read the summary
- Industry, p16
Read the report
- Industry, p124
- Source of GHG emissions
- GHG mitigation options
- Influence of long term ambitions on near term actions and pathways
- Co-benefits
- Insights on enabling policies
- Case studies
- Knowledge gaps

